
Can Physical Therapy Fix a Herniated Disc?
Disc herniation can lead to significant discomfort and limitations in daily activities, but physical therapy offers a promising path to relief and recovery. By focusing on targeted exercises and therapeutic techniques, physical therapy aims to alleviate pain, restore function, and strengthen the spine’s support structures.
In this article, we’ll explore how physical therapy can be an essential component in managing and overcoming a herniated disc.
What Is A Herniated Disc?
First, what is a herniated disc?
Discs are small, circular cushions between the bones in the spine (vertebrae). A herniated disc happens when discs in the spine bulge from their proper place. This issue is most common in the lower spine or lower back, though it can occur in other areas of the spine as well.
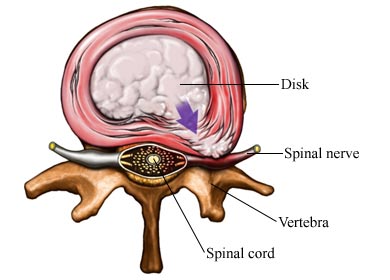
Herniated Disc Risk Factors
Herniated discs can develop when discs lose water content, become flatter, and provide less cushioning. It may also occur when the disc is physically damaged by trauma.
Several factors can increase your risk of developing a herniated disc:
- Age: Our chances of experiencing a herniated disc increase as we age, particularly past 30.
- Trauma: Falls, accidents, or sudden twisting movements can lead to disc herniation.
- Strain: Repeated or sudden strain, such as lifting heavy objects without proper technique, can contribute to herniation.
- Wear & Tear: Jobs involving physical demands or being overweight can accelerate disc degeneration.
Symptoms of Herniated Discs
The symptoms of a herniated disc can vary depending on the location and size of the herniation.
Common symptoms include:
- Pain: This can range from sharp and piercing to dull and aching, and may radiate over the back, buttocks, down the back of one thigh, and into the calf. Pain may affect one or both legs.
- Numbness or Tingling: You might experience numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs, feet, or arms.
- Neck Pain: In cases where the herniated disc is in the neck, you may experience sudden aching that makes movement painful.
- Severe Discomfort: In extreme cases, you may struggle to find comfort, even when lying down.
Treating a Herniated Disc
Treating a herniated disc involves a multifaceted approach aimed at relieving pain, improving function, and supporting the spine to prevent further issues.
Here’s an overview of the key strategies used in managing a herniated disc:
Initial Conservative Treatment
- Rest and Activity Modification: Initially, it’s crucial to rest and avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Modifying daily activities to avoid movements that strain the spine can help reduce inflammation and prevent further injury.
- Pain Management:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications or muscle relaxants.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat can help relax tense muscles and improve blood flow, while cold packs can reduce inflammation and numb the affected area.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is a cornerstone of treatment for a herniated disc. The primary goals are to alleviate pain, restore function, and strengthen the supporting muscles around the spine.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting healthier habits can support the healing process and prevent future issues. This includes maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and incorporating regular exercise.
Advanced Treatments
- Injections: If conservative treatments are not effective, spinal injections may be considered. Epidural steroid injections can reduce inflammation around the affected nerve roots, providing temporary relief and allowing for more effective participation in physical therapy.
- Surgical Options: Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there is severe nerve compression leading to significant functional impairment.
Post-Surgery Rehabilitation
If surgery is required, post-surgery rehabilitation is essential for recovery.
This phase includes:
- Rehabilitation Exercises: Designed to restore strength and range of motion while ensuring proper healing.
- Education: Teaching proper body mechanics and posture to prevent future injuries.
- Ongoing Physical Therapy: Helps to regain function and improve overall spinal health.
Long-Term Management
Managing a herniated disc long-term involves:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling to maintain spinal health.
- Continuous Strengthening and Flexibility Work: Incorporating exercises that strengthen the core and maintain flexibility in the spine.
- Regular Check-ups: Monitoring the condition with your healthcare provider to address any recurring issues promptly.
Treating a herniated disc involves a combination of conservative measures, physical therapy, and, if necessary, advanced treatments or surgery. Early intervention, along with a comprehensive treatment plan, can significantly improve outcomes and help you return to a more comfortable and active life.
Physical Therapy for Herniated Discs
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing and recovering from a herniated disc. While it doesn’t “fix” the disc itself, it is instrumental in improving quality of life by reducing pain, enhancing mobility, and strengthening the supporting muscles around the spine.
Here’s what you need to know about physical therapy for a herniated disc:
Can You Fix a Herniated Disc with Physical Therapy?
Physical therapy cannot reverse a herniated disc to its original state. Instead, its primary aim is to alleviate the symptoms and functional limitations caused by the herniation.
Through a combination of targeted exercises, manual therapy, and patient education, physical therapy helps to reduce the pressure on the affected nerve roots, thereby decreasing pain and improving overall function.
To address pain and stiffness associated with a herniated disc, physical therapy incorporates a variety of techniques and exercises, including:
- Traction: Helps alleviate pressure on the spine and reduce pain.
- Heat Therapy: Relieves muscle tension and promotes blood flow to the affected area.
- Cold Therapy: Reduces inflammation and numbs pain in the affected region.
- Spinal Mobilizations: Enhances spinal movement and reduces stiffness.
- Strengthening Exercises: Focus on building muscle strength to support and stabilize the spine.
- Stabilization Exercises: Improve spinal stability and prevent future injury.
Can Exercise Repair a Herniated Disc?
Exercise alone cannot repair the herniated disc, but it is essential for a successful recovery. The primary goal of exercise in physical therapy is to support the spine, improve posture, and reduce the strain on the affected disc.
- Strengthening Exercises: These exercises target the muscles that support the spine, including the core and lower back muscles. A stronger core can help better support and stabilize the spine, reducing the load on the herniated disc and potentially alleviating some of the symptoms.
- Stretching Exercises: Stretching helps to relieve tension in the muscles surrounding the spine, which can reduce pain and improve flexibility. By increasing the range of motion and reducing muscle tightness, stretching can help improve overall spinal function and comfort.
In essence, while exercise does not directly repair the disc, it can significantly enhance spinal health, reduce pain, and improve mobility, making daily activities more manageable.
When Should I Start Physical Therapy for a Herniated Disc?
The timing of physical therapy can significantly impact the recovery process. It is generally recommended to begin physical therapy as soon as possible after diagnosis.
Early intervention helps to manage pain more effectively, prevent the condition from worsening, and initiate the strengthening of spinal support muscles.
- Early Intervention: Starting physical therapy early can prevent further deterioration and may lead to quicker relief from symptoms. Immediate therapy can help reduce inflammation, improve spinal alignment, and start the process of strengthening and mobilizing the affected areas.
- Severity and Overall Health: The exact timing of physical therapy may vary depending on the severity of the symptoms and your overall health. For some, therapy may start immediately after the initial diagnosis, while others may begin after an initial period of conservative treatment or after more severe symptoms are managed.
The 4 Phases of Physical Therapy in Rehabilitation
The rehabilitation process for a herniated disc typically involves several phases:
- Pain Relief and Initial Care: Initially, the focus is on relieving pain and inflammation. This may include techniques such as ice application, heat therapy, and gentle stretching.
- Restoration of Mobility: As pain subsides, physical therapy will focus on restoring range of motion and flexibility. Gentle stretching and low-impact exercises can help improve spinal flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Strengthening Exercises: Once you are able to move more comfortably, strengthening exercises are introduced to support the spine and prevent future issues. Core strengthening exercises are particularly important as they help stabilize the spine and reduce the load on the discs.
- Functional Training and Prevention: The final phase involves functional training to help you return to your daily activities. Your therapist will also provide education on proper body mechanics and posture to prevent future injuries.
Did you know you have Direct Access* to Physical Therapy? No referral, no problem!
While physical therapy cannot reverse a herniated disc, it plays a vital role in managing the condition and improving quality of life. By addressing pain, improving function, and strengthening the supporting muscles, physical therapy can help you lead a more comfortable and active life.
If you suspect you have a herniated disc, consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action, which may include physical therapy to aid in your recovery.
Ready to get started? Check out one of our 18 locations to get started today!
Want more content from TJC? Check us out on Instagram!


















